BASIC TERMINOLOGY OF HTML AND CSS
THE THREE LANGUAGES OF THE FRONT-END
WHAT IS HTML?
👉HyperText Markup Language.
👉 HTML is a markup language that web developers use to structure and
describe the content of a webpage (not a programming language).
👉 HTML consists of elements that describe different types of content:
paragraphs, links, headings, images, videos, etc.
👉 Web browsers understand HTML and render HTML code as websites.
ANATOMY OF AN HTML ELEMENT
👉Cascading Style Sheets
👉 CSS describes the visual style and presentation of the content
written in HTML
👉CSS consists of countless properties that developers use to format
the content: properties about font, text, spacing, layout, etc.
HOW WE SELECT AND STYLE ELEMENTS
A CSS RULE
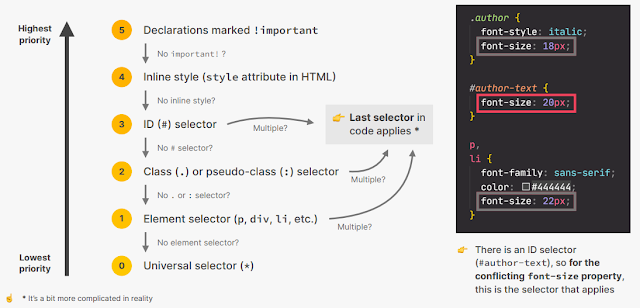
CONFLICTING SELECTORS AND DECLARATIONS
RESOLVING CONFLICTING DECLARATIONS
👉Content: Text, images, etc.
👉 Border: A line around the element,
still inside of the element
👉 Padding: Invisible space around the
content, inside of the element
👉 Margin: Space outside of the
element, between elements
👉 Fill area: Area that gets filled with
background color or background
images
ANALOGY FOR THE CSS BOX MODEL
ELEMENT HEIGHT AND WIDTH CALCULATION
Final element width = left border + left padding +
width + right padding + right border
Final element height = top border + top padding
+ height + bottom padding + bottom border
👉 We can specify all these values using CSS properties
👉 This is the default behavior, but we can change it
BLOCK-LEVEL ELEMENTS
👉 Elements are formatted visually as blocks
👉 Elements occupy 100% of the parent element’s width,
no matter the content
👉 Elements are stacked vertically by default, one
after another
👉 The box model applies as shown earlier
INLINE ELEMENTS
👉 Occupies only the space necessary for its content
👉 Causes no line-breaks after or before the element
👉 Box model applies differently: heights and
widths do not apply
👉Paddings and margins are applied only
horizontally (left and right)
















Comments
Post a Comment